Color Management in VFX - Part I: Overall
- How color flows in the post production
In the VFX industry, many professionals are not very familiar with color management. To be honest, it scares them, and they don’t even know where to start understanding color. They also don’t understand why colors always look different, so they end up trying to force colors to match without any unified color management.
Understanding color is crucial in the VFX production process, yet it’s often overlooked. A solid color management workflow can double everyone’s efficiency and avoid the difficulty of making corrections later on. On the other hand, not having a unified workflow can make the work much more challenging. Before we dive in, let’s go over some basic concepts to clear up any misunderstandings or unfamiliar areas.
All the concepts here have been simplified to have a picture of the whole idea for the artists to understand easily. I try not to use terms that are too incomprehensible.
What we will mention in this article:
WHAT IS COLORSPACE?
There are three important parameters that define the colorspace: Gamma, Gamut and White Point.
Let’s look at the graphs, gamma is a non-linear operation to encode and decode the illuminance, by taking advantage of the non-linear manner in which humans perceive light and color; Gamut is defined by the three primaries including red, blue and green, which at each top of the triangle in the graph; And we still need to define which point is the brightest and purest white, that we so called the white point.
Every colorspace has its own definition in gamma, gamut and white point for different purposes and scenario like the example in the graphs: sRGB has three primaries at the top of the red triangle which comes from Rec.709 and reflect the approximate color of consumer CRT phosphors; it has been designed to be seen in the dim light environment which defines the white point as D65, a standard illuminant has color temperature of approximately 6500K. Its non-linear curve is similar to the gamma response of a CRT and efficiently reflects the color of human-discernible light levels.
WHAT IS IT ALL ABOUT IN VFX?
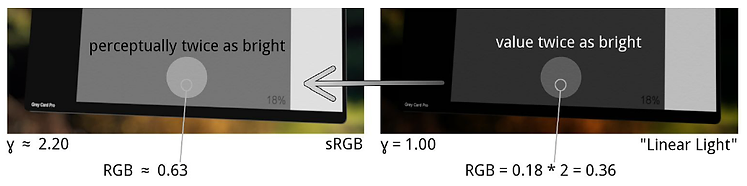
If we put a middle grey as 0.5 under the sRGB colorspace, it will be 0.18 in the linear space. And here is the problem, in the linear space everything is calculated linearly like how lights work in the real world. Let’s double the intensity, so 0.18 becomes 0.36 and convert the value back to sRGB colorspace as 0.63.
OK, let’s go back to do the same thing: double the intensity for the middle grey 0.5 in sRGB colorspace and we got 2, which obviously is not equal to the value 0.63 calculated from the linear space. The result shows the difference doing the same operation in the linear and sRGB space. This is why we need to linearize all the files with non-linear gamma curves.
Cool. So now we know working in visual effects we need to keep two things in mind:
Linearize everything
Set a proper gamut and make sure all sources are interpreted using the same primaries and white point.
DIFFERENT LINEAR WORKFLOW
Now we start with the whole workflow. Before the ACES jump into the game, the basic concept is around keeping the colorspace consistent in every step.
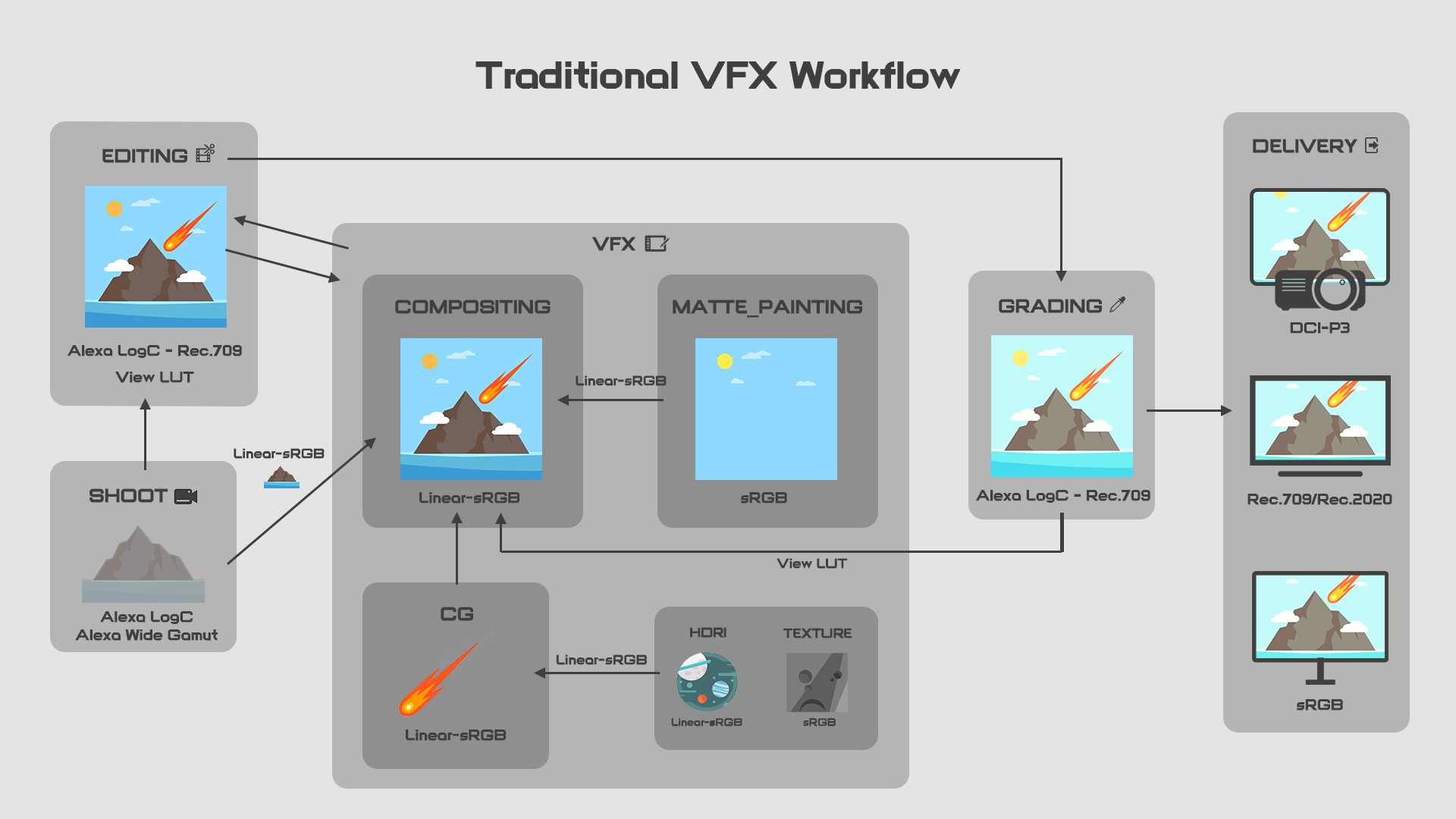
In the traditional workflow, the most commonly used colorspace in VFX is linear-sRGB. From all the assets for CG artists need to linearize the sRGB images before doing computation. It is the option for matte painters to linearize sRGB images or not depending on studios. In compositing, compers convert log footage back to linear-sRGB then they are able to combine other elements from the CG department and matte painting department in the same linear-sRGB colorspace. That will ensure mathematically accuracy in all processes.
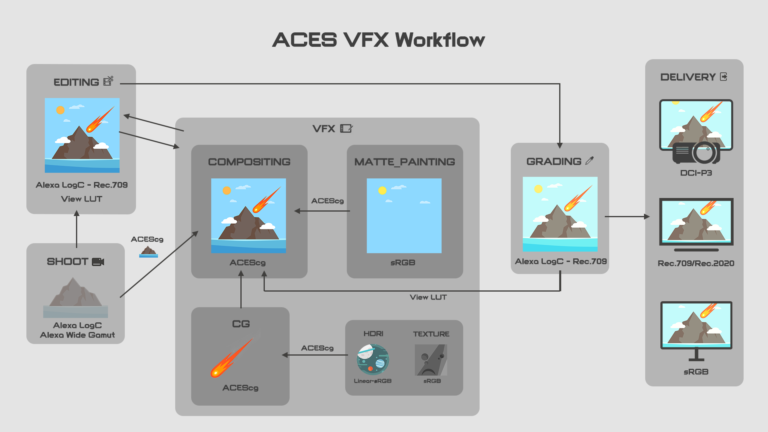
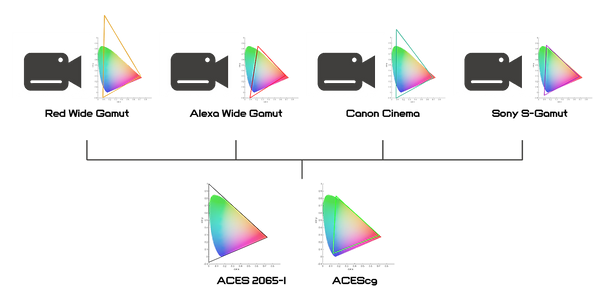
Alright, let’s get into the ACES workflow. In fact all the steps are pretty much the same. The major difference is it maps the sRGB primaries to ACEScg, which allows different color settings in different cameras from their own manufacturers can be converted into the same giant colorspace and artists have better control to manipulate color in the larger gamut with high dynamic range.
sRGB vs ACES
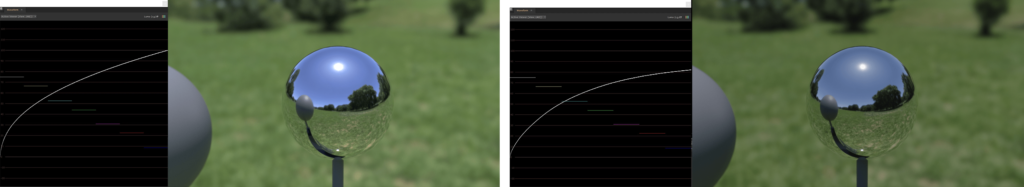
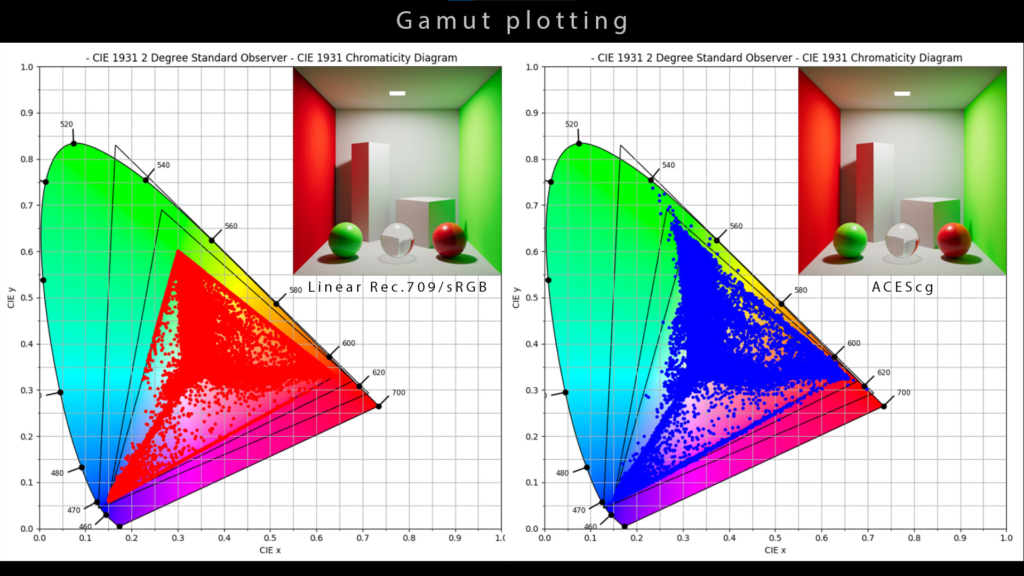
The limitation for the traditional linear workflow is the primaries only confined in sRGB gamut, which means pixels from objects in 3D applications receive and respond lights will also be clipped in the sRGB gamut. As the graphs below, we can see it has no rolloff in the highlight area in linear-sRGB and that will cause overexposure and over-saturation in our images.
Here is the better explanation from Chris Brejon’s website. Chris Brejon is a ACES mentor and he wrote amazing context about CG cinematography. Probably need some patience and time to digest but please check it out.
So the color model is plotted in CIE-XYZ and flatten to a locus. the first image is rendered in linear-sRGB. As we mentioned earlier, all the colors have been confined in sRGB gamut, you can see it appears somewhat over-saturated in the area where the light hits. On the other hand the second image has a much better look with rolloff in highlight in ACEScg gamut especially the green pixels.
OK. A brief conclusion for this short paragraph. If CG Artists use sRGB textures and linear-sRGB working space in their 3D applications, the colors in the output images will be confined to the sRGB gamut. In the ACES working space, images will look more realistic with a larger gamut and higher dynamic range.
ACES in PRODUCTION
We have introduced the traditional linear workflow and ACES workflow and we pretty much cover the idea for the CG part why we want to use ACES. Let’s recall the workflow diagrams and take some steps back to the shooting part.
How does ACES affect the production part?
We both know there are a bunch of professional cameras for filming and these manufactures have their own transfer functions(log) and gamuts. In the traditional workflow we need to interpret the footage correctly to have accurate calculation and composite with other elements. But here is also the important step that many artists get confused by. Again we take alexa as the example. How do we convert alexa footage into the same colorspace as CG render?
- Apply the transfer function to neutralize the footage from logc into linear space.
- Convert Alexa Wide Gamut(AWG) into sRGB.
Here is the catch. Lots of artists do not understand the 2nd point therefore they are doing their artistic work in the linear-AWG space instead of linear-sRGB. Well, in many cases, clients don’t care and never get kickbacks and everything is fine. But if you want to know why your CG looks fake, it’s better to understand these steps then you will know how to improve it.
In the ACES workflow, your applications will convert the footage whatever its gamut is into ACES and for the rest, all you need to do is apply gamma correction. Awesome. The main purpose is to integrate different footage from different cameras into a vast colorspace that you don’t have to worry about having the wrong interpretation.
COMPOSITING in ACES
We have talked about ACES in CG and shooting. It shouldn’t be too complicated now if you’ve grasped the concept above.
As a compositor, you will definitely feel great if you get all the elements with the maximum capacity. You know the feeling like a chef with access to the finest ingredients and seasonings. Once you have footage and CG in ACES, you just need to put them into another application in the ACES working space and do your compositing. Easy, right? However, we know the idea of ACES, but how do we know exactly what to do in Nuke? I’ll break down the steps in detail in the next post.
Color management is a big topic to me and I am still learning it, please correct me if there is any inaccurate.